Complete Guide to Sleep
Sleep is a fundamental aspect of human health, influencing our physical and mental well-being. This comprehensive guide explores the science behind sleep, its benefits, potential risks, and practical tips for improving sleep quality.
What is Sleep?
Sleep is a natural, recurring state of rest that is essential for the body and mind. It is characterized by altered consciousness, reduced sensory activity, and inhibition of nearly all voluntary muscles. Sleep is vital for maintaining cognitive skills, emotional regulation, and overall health.How Does Sleep Work?
Sleep involves complex biological processes and is regulated by the circadian rhythm—our internal body clock. The sleep cycle consists of REM (Rapid Eye Movement) and non-REM stages, each serving different functions. Non-REM sleep, which includes stages 1-4, is crucial for physical recovery and immune function, while REM sleep supports brain function, mood regulation, and memory consolidation.- Circadian Rhythm: Controls sleep-wake cycles, influenced by light and darkness.
- Sleep Stages: Alternating between REM and non-REM, each with distinct physiological functions.
Benefits of Sleep
Quality sleep offers numerous benefits, including:- Cognitive Function: Enhances learning, memory, and problem-solving skills.
- Emotional Well-being: Supports mental health by reducing stress and anxiety.
- Physical Health: Boosts immune function, reduces inflammation, and aids muscle recovery.
- Longevity: Consistent sleep patterns contribute to a longer, healthier life.
Potential Risks and Side Effects
Sleep deprivation and disorders can have adverse effects, such as:- Cognitive Impairment: Difficulty concentrating, memory lapses, and decision-making issues.
- Mental Health Issues: Increased risk of depression and anxiety.
- Physical Health Problems: Higher risk of obesity, diabetes, cardiovascular diseases, and weakened immune system.
How to Improve Sleep Quality
Practical tips for better sleep include:- Create a Sleep-friendly Environment: Keep your bedroom dark, cool, and quiet.
- Establish a Routine: Go to bed and wake up at the same time every day.
- Limit Screen Time: Avoid screens at least an hour before bedtime.
- Mindful Practices: Engage in relaxation techniques like meditation or deep breathing.
What the Research Says
Research underscores the importance of sleep for overall health. Studies have linked adequate sleep to improved cognitive and physical performance, while chronic sleep deprivation is associated with numerous health issues. However, ongoing research continues to explore the nuances of sleep's impact on different populations and individual variations.Who Should Consider Sleep?
Adequate sleep is crucial for everyone, but certain groups particularly benefit:- Children and Adolescents: Essential for growth and development.
- Elderly: Supports cognitive function and reduces fall risk.
- Athletes: Enhances performance and recovery.
Related Conditions
Sleep disorders such as insomnia, sleep apnea, and restless legs syndrome can significantly impact quality of life. Addressing these conditions often requires medical intervention and lifestyle changes.Frequently Asked Questions
- How much sleep do adults need?
- Is it possible to catch up on sleep debt?
- Can naps replace a full night's sleep?
- What are common signs of sleep deprivation?
Key Takeaways
- Sleep is vital for physical, mental, and emotional health.
- Understanding and maintaining a balanced sleep schedule can prevent health issues.
- Practical steps can significantly improve sleep quality.
- Ongoing research continues to reveal sleep's complex role in health and well-being.
Related Articles
3 articles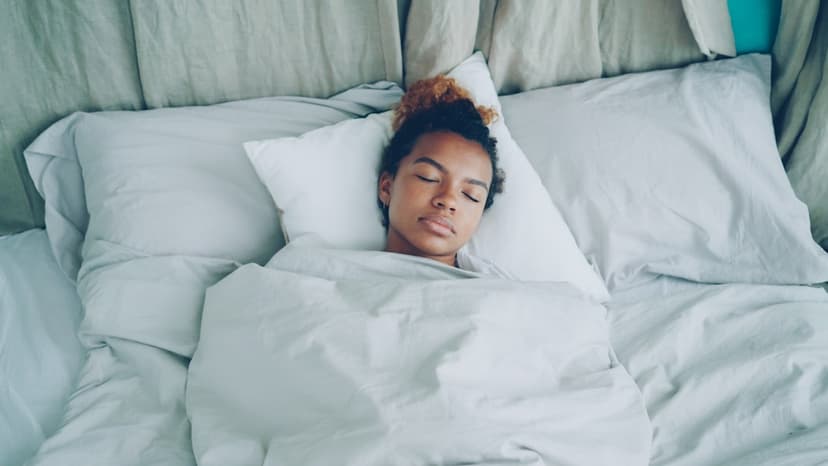
Perfecting Sleep: Tools From Huberman and Walker
In this Huberman Lab Essentials conversation, Dr. Matt Walker frames sleep as the most effective way to reset brain and body health, and he treats sleep stages as non-negotiable biology. The discussion walks through a typical night of non-REM and REM cycles, why early-night deep sleep and late-night REM matter differently, and why sleep quality is as important as quantity. It also offers actionable levers that do not require pills, especially morning daylight, caffeine timing, and avoiding alcohol or THC near bedtime. Melatonin is positioned as a timing signal, not a strong sleep generator for most healthy adults.

Mindset, Mindfulness, and Sleep, Dr. Ellen Langer
Dr. Ellen Langer’s perspective flips a common sleep message on its head: your body is not a machine that responds only to inputs like hours slept, exercise minutes, or perfect routines. It also responds to meaning, expectations, labels, and what you notice. In this Huberman Lab conversation, Langer argues that “mindfulness” is not meditation, it is active noticing, and it can alter health outcomes, including sleep, healing, and aging markers. The practical takeaway is not magical thinking, it is learning to treat health “facts” as probabilities, reducing sleep anxiety, and training yourself to notice variability so you regain agency.
Should You Wear a Cast, Brace, or Sling at Night?
Trying to sleep with a sling, boot, or knee immobilizer can feel impossible, until you realize why nighttime is often the riskiest time to go without it. This article follows the video’s practical, injury-by-injury approach: do what your clinician instructed, and if you are unsure, lean toward wearing it at night until you confirm. You will learn which injuries most often need nighttime immobilization (like shoulder injuries, Achilles rupture, and certain knee fractures), when it may become optional, and simple comfort hacks like cleaning and covering removable braces.
Glossary Definition
Sleep is a natural state of rest for the body and mind, essential for health.
View full glossary entryHave questions about Complete Guide to Sleep?
Ask Clara, our AI health assistant, for personalized answers based on evidence-based research.